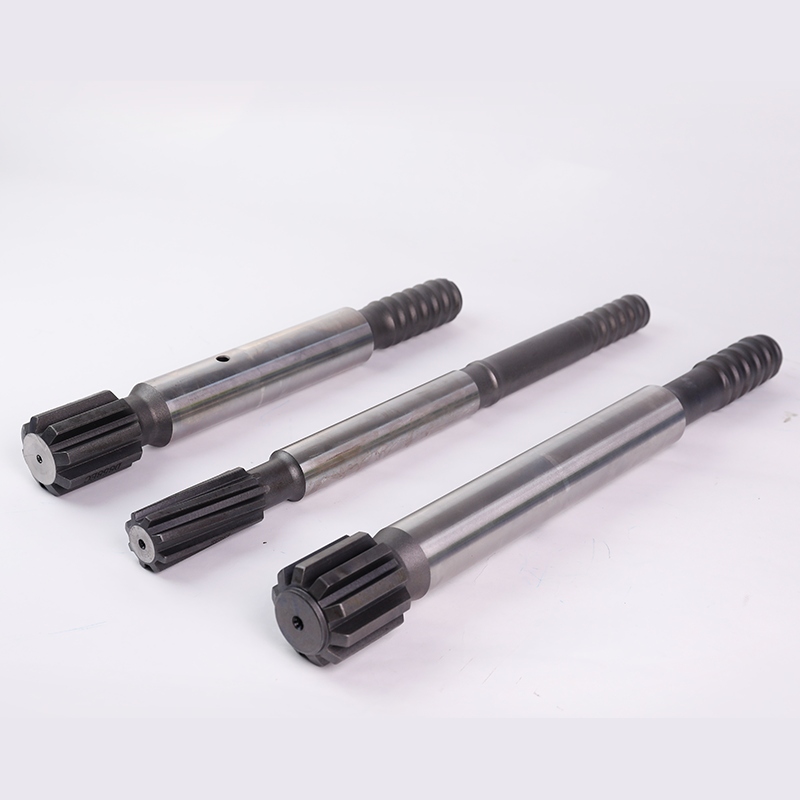
In rock drilling operations, efficiency and tool longevity are critical factors that directly affect project costs and productivity. One of the essential components in rock drilling systems is the shank adapter, a crucial transmission connection between the rock drill and the drill rod. The primary function of the shank adapter is to withstand the impact energy and torque transmitted by the rock drill, ensuring effective energy transfer for drilling.
Given the harsh working conditions of rock drilling, shank adapters are among the most frequently replaced consumables in drilling operations. However, frequent failure does not always mean inevitable scrapping—many issues arise due to component wear, improper maintenance, or incorrect drilling techniques. By identifying and addressing these failures early, the lifespan of shank adapters and other drilling tools can be significantly extended.
In this article, we will explore:
- Types of Shank Adapters
- Common Causes of Shank Adapter Failures
- 13 Practical Solutions to Improve Shank Adapter Longevity
Types of Shank Adapters
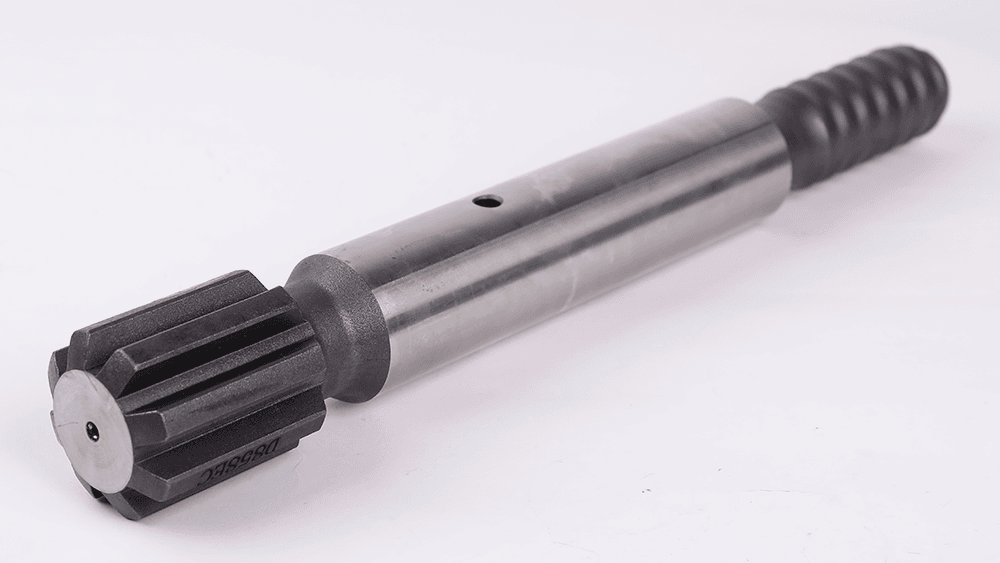
Shank adapters come in different designs, each suited for specific drilling applications and rock drill models. The three most common types include:
1. Flange-Type Shank Adapter
- Cross-Section: Hexagonal
- Inscribed Circle Diameter: 22mm or 25mm
- Length: 108mm or 159mm
- Manufacturing Process: Forged
- Application: Used in light rock drills
Flange-type shank adapters are designed for small rock drills where weight and maneuverability are crucial. Their hexagonal shape provides better grip and energy transfer in lightweight drilling systems.
2. Lug-Type Shank Adapter
- Drill Rod Diameter: 25mm or 32mm
- Application: Designed for medium-sized guide-type rock drills with internal rotation
Lug-type shank adapters are more robust than flange-type adapters and are commonly used in medium-sized rock drills that require more rotational stability and torque resistance.
3. Spline-Type Shank Adapter
- Drill Rod Diameter: More than 38mm
- Manufacturing Process: Machined
- Application: Suitable for heavy-duty guide-type external rotating rock drills
Spline adapters are the most robust among the three, designed for heavy-duty drilling operations where high torque is required. These adapters ensure efficient energy transmission in large-scale mining and tunneling projects.
Common Causes of Shank Adapter Failures
Although shank adapters are made from high-strength materials, they are subject to extreme mechanical stress, leading to failure over time. The most common reasons for failure include:
- Component Wear – Over time, bushings, chuck drivers, and coupling sleeves wear out, leading to misalignment and excessive stress on the shank adapter.
- Lack of Lubrication – Inadequate lubrication increases friction, leading to overheating, spline damage, and shortened service life.
- Excessive Feed Force – High drilling pressure can cause fractures and premature wear, especially on splines and threads.
- Heavy Rotational Torque – When torque is too high, it accelerates wear and can lead to spline or thread failure.
- Improper Alignment – A misaligned drill string due to worn-out bushings or deviation in the drill hole can cause impact marks, chipped corners, and other structural damage.
- Overuse of Coupling Sleeves – Reusing worn coupling sleeves weakens the connection, leading to increased stress and failure in both the adapter and drill rod.
- Drilling in Soft or Broken Ground – Excessive rotation in such conditions increases wear on splines and threads, leading to pitting and galling.
13 Practical Solutions to Improve Shank Adapter Longevity
To extend the lifespan of shank adapters and reduce operational costs, it is essential to follow proper maintenance practices and implement corrective measures when failures occur. Below are 13 common issues and their respective solutions:
1. Impact Marks, Chipped Corners, and Mushrooming at the End
- Cause: Misalignment due to worn bushings.
- Solution: Replace worn components to ensure proper alignment and energy transfer.
2. Failure Approximately 25mm from the Strike Face
- Cause: Worn chuck driver.
- Solution: Replace worn chuck driver to maintain a secure fit and avoid excessive stress on the shank adapter.
3. Failure at the Top of the Spline Due to Lack of Lubrication
- Cause: Inadequate grease application.
- Solution: Lubricate rock drills regularly to minimize friction and prevent premature wear.
4. Failure at the Top of the Spline Due to Excessive Feed Force
- Cause: Overloading the drilling system.
- Solution: Monitor coupling temperatures and adjust feed pressure according to manufacturer recommendations.
5. Failure at the Top of the Spline Due to Worn Chuck Driver or Front Bushing
- Cause: Excessive play in the system.
- Solution: Replace worn chuck driver and front bushing to maintain drilling precision.
6. Failure Across Splines Due to Heavy Rotational Torque
- Cause: Excessive twisting forces.
- Solution: Adjust drilling pressures to prevent unnecessary strain on the adapter.
7. Wear on the Bottom of the Spline Shoulder Due to Excessive Rotation When Retracting String
- Cause: Excessive rotational movement during retraction.
- Solution: Adjust drilling pressures to optimize retraction without additional stress.
8. Failure at the Front Head Due to Misalignment
- Cause: Worn front bushing causing drilling deviation.
- Solution: Replace worn components to maintain accuracy and prolong tool life.
9. Failure Above Threads Due to Hole Deviation
- Cause: Misalignment during drilling.
- Solution: Use straight-hole drilling devices or systems to maintain precision and prevent uneven stress distribution.
10. Failure in the Main Body of Threads Due to Excessive Coupling Sleeve Usage
- Cause: Repeated use of worn coupling sleeves.
- Solution: Replace worn coupling sleeves and avoid reusing old ones with new drill rods.
11. Chipped Thread End Due to Improper Coupling to the Drill Rod
- Cause: Poor connection between the shank adapter and drill rod.
- Solution: Replace damaged or worn coupling sleeves to ensure a secure connection.
12. Chipped Thread End Due to an Uneven Drill Rod End
- Cause: Poorly manufactured or damaged drill rod ends.
- Solution: Send for analysis and consider replacing improperly machined drill rods.
13. Pitting and Galling on Splines Due to Excessive Rotation in Soft or Broken Ground
- Cause: High-speed rotation in unstable formations.
- Solution: Adjust drilling pressure to match ground conditions and reduce wear.
Key Takeaways
From the above solutions, it is evident that shank adapter failures are often linked to the wear or damage of other drilling components. To improve the efficiency and service life of shank adapters, it is essential to:
- Regularly inspect and lubricate rock drilling components to prevent excessive wear.
- Monitor drilling parameters to avoid overloading and unnecessary torque stress.
- Use high-quality shank adapters from reliable manufacturers to ensure durability and performance.
- Replace worn-out accessories promptly to maintain the integrity of the entire drilling system.
The shank adapter plays a crucial role in drilling efficiency, and its quality directly affects the service life of the drill rod. Therefore, investing in high-quality shank adapters and following proper maintenance practices will significantly improve overall rock drilling performance and cost-effectiveness.





